| Improving the solubility of Mn and suppressing the oxygen vacancy density in Zn0.98Mn0.02O nanocrystals via octylaminetreatment |
| From: PublishDate:2013-06-15 Hits: |
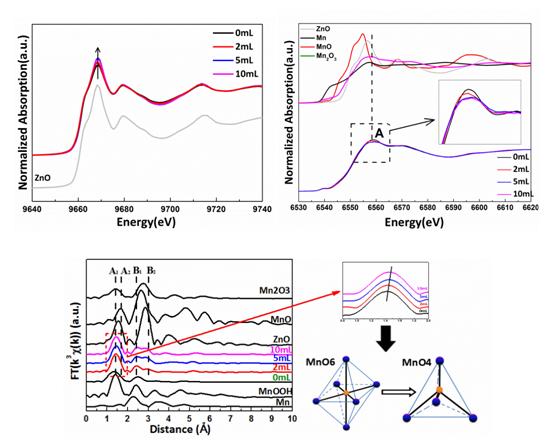
Mn-doped ZnO has been investigated extensively due to the potential applications as spintronics materials. However, the solubility of Mn in ZnO is lower in the nanocrystals than that in the bulk because of self-purification process of Mn ions.In addition, some defects such as oxygen vacancy (VO) can be easily formed due to the low formation energy during doping. The presence of VO has great effects on the properties of Mn-doped ZnO. It is very important to find an effective method of enhancing the solubility of Mn and suppressing the formation of VO in Mn-doped ZnO.Co-doping can modify the state of the dopants in host lattices and modulate the defect type and concentration. In ZnO system, transition metal Mn doping form a donor level, while N doping form an acceptor level, we suppose that Mn-donor level and N-acceptor level may form the donor-accepter-donor (D-A-D) complex, which could increase the solubility of Mn in ZnO during (Mn, N) co-doping by reducing the ionization energy of the donor impurities.However, it is difficult to measure the solubility and the defects type and concentration. X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) is very sensitive to the local environment of a selected atom. We collected Mn and Zn k-edge XAFS spectra on Beamline 1W1B at the Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility (BSRF).
The result of Zn k-edge X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) reveals that the VO density deceases with increasing treatment octylamine content. The variation of Mn k-edge XAFS indicates that octylamine treatment can change the state of Mn in the ZnO lattice, from Mn3+O6 in the interstitial sites to Mn2+O4 with tetrahedral coordination in the substitutional sites. It means that more and more Mn2+ ions dissolve into ZnO lattices with increasing treatment octylamine content. We have clearly demonstrated that co-doping with N can enhance the solubility of Mn in ZnO and suppress VO density in Zn0.98Mn0.02O nanocrystals. This result indicates that we can effectively investigate the local environment and the defect type and concentration via XAFS spectra.
Article: Yan Cheng,WeichangHao,*HuaizheXu,*YouXing Yu,Tianmin Wang,Rui Chen,Linjuan Zhang,Y. Du,X. L. Wang,and S. X. Dou. Improving the solubility of Mn and suppressing the oxygen vacancy density in Zn0.98Mn0.02O nanocrystals via octylamine treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2012, 4, 4470-4475. |
|
|
| Chinese
Science Highlights
Home /
Copyright © 2011 - 2012 Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility