| Local Fine Structural Insight into Mechanism of Electrochemical |
| From: PublishDate:2017-06-16 Hits: |
Almost all metal materials are in the state of thermodynamic instability because of aggressive service environments, and their corrosion failures even cause many serious accidents such as fire and explosion etc. For improving the corrosion resistance of metal materials, passive metal surface tends to form a layer of stable, adherent, tenacious, and permanent solid oxide film to achieve steady state. However, the evolution mechanism of passivation on atomic scale is still unclear. Therefore, a team from national center for materials service safety of University of Science and Technology Beijing has gained insight into the structure and corrosion resistance of titanium passive film by AES, XPS, XAFS and electrochemical measurements. And their research has been published on July 20th, 2016 in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. A series of XANES and EXAFS spectra at Ti K-edge were collected from the passive films using synchrotron radiation at BSRF. Quantitative X-ray absorption near edge structure analysis of the local electronic structure of the topmost surface shows that the chemical states of oxides in passive film changes greatly with the applied potential, because the ratio of [TiO2]/[Ti2O3] is consistent with that of passivation/dissolution of electrochemical activity, which is validated by XPS measurements. Theoretical calculation and analysis of extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectra indicate that the increase of average Ti?O coordination causes the electrochemical passivation, and the dissolution is due to the decrease of average Ti?Ti coordination. Besides, the local fine structure variation affects the distribution and migration of the micro defects in the passive film, which further changes the corrosion resistance of the applied metal in severe media. The results are in good agreement with the prediction of point defect model (PDM).
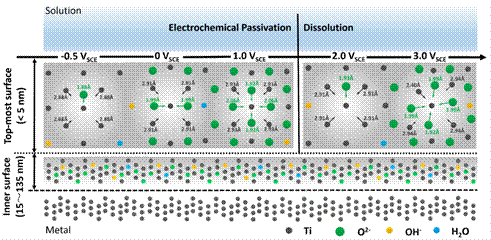
Figure 1. Schematic representation of local fine structure of titanium passive film This research opens the way for further studies of the evolution mechanism of passivation during metal materials corrosion, and provides scientific clues to develop the corrosion theory and protection technique. "Corrosion is complex and meaningful, which can be controlled efficiently unless the mechanism is clear. Combined local fine structure with corrosion resistance, this work elucidates the mechanism of electrochemical Passivation. Such a study is the basis of metal self-protection and lays the theoretical and experimental foundation for the precise description of metal corrosion and the practical application of passive metals. And BSRF provides strong support for this study." says Dongbai Sun, the team leader and the professor of national center for materials service safety of University of Science and Technology Beijing. Article: Lu Wang,* Hongying Yu,* Ke Wang, Haisong Xu, Shaoyang Wang, and Dongbai Sun. Local Fine Structural Insight into Mechanism of Electrochemical Passivation of Titanium. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(28): 18608-18619. |
|
|
| Chinese
- Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting——Top ten major scientific progresses in China in 2015
- The nano-resolution imaging platform was awarded the first rate prize of Beijing Science and Technology in 2014
- Beamline 1W1 of BSRF started to runoperate in the couplingparasitic mode of BEPCII
- Synthesis of High Performance Polymer Materials for Field Effect-Transistors
- Surfactant molecular aggregates in green solvents
- GIXRD has played an important role in the characterization of organic thin-film transistors
Copyright © 2011 - 2012 Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility