| Synthesis of Co–Sn Intermetallic Nanocatalysts toward Selective Hydrogenation of Citral |
| From: PublishDate:2017-06-16 Hits: |
Selective hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes to corresponding unsaturated alcohols is an important reaction in the production of fine chemicals. Co-based intermetallic compounds (IMCs) materials have recently been explored in the selective hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes with good performances. However, the conventional preparation method of Co-based IMCs normally suffers from rigorous conditions, noxious organic reagents or uncontrollable structure/composition; and uncover the structure–property correlation still remains a huge challenge. A team from Beijing University of Chemical Technology has developed a facile and green strategy for the preparation of Co-based IMCs catalysts and provided a deep insight into structure–property relationship. Their research has been published on July 23th, 2016 in Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
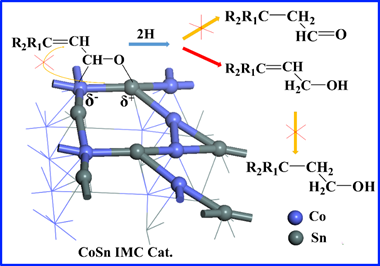
Scheme 1. Schematic illustration of selective hydrogenation of α, β-unsaturated aldehydes on CoSn IMC. Three supported Co–Sn intermetallic compound (IMC) catalysts (Co2.9Sn2, CoSn and CoSn2) with a particle size of ~20 nm were prepared via a modified LDH approach (impregnation-coreduction method), which exhibit largely enhanced catalytic activity and selectivity toward selective hydrogenation of citral. The results of experiment-calculation combination study reveal that the introduction of Sn in Co–Sn IMCs dramatically optimizes the geometric and electronic structures of active Co, in which Sn isolates the Co active-site and electron transfer occurs from Sn to the Co atom that weaken the hydrogenation of the C=C group, accounting for the largely enhanced hydrogenation selectivity of citral to unsaturated alcohols.
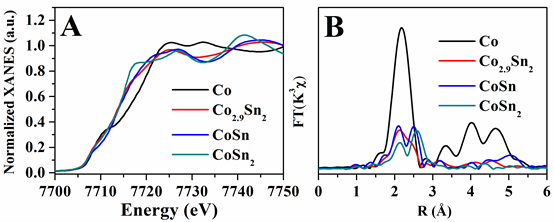
Figure 1. (A) Normalized intensity of Co K-edge XANES spectra for the Co–Sn IMCs and Co foil; (B) corresponding Fourier transform k3-weighted EXAFS spectra in R space compared with Co foil. Using synchrotron radiation at BSRF, the charge transfer from Sn to Co was identified. The Co atoms are gradually dispersed by Sn atoms through the Co–Sn coordination along with the increase of the Sn/Co ratio. In this work, efficient catalysts for selective hydrogenation of citral was prepared and structure-property correlation between the structure of active sites and the catalytic performance was revealed. The design and preparation of Co-based IMCs catalysts can be extended to other bimetal catalysts with largely enhanced selectivity.
Article: Junyao Zhou, Yusen Yang, Changming Li, Shitong Zhang, Yudi Chen, Shuxian Shi,* Min Wei*, Synthesis of Co–Sn Intermetallic Nanocatalysts toward Selective Hydrogenation of Citral, J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 12825-12832. |
|
|
| Chinese
- Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting——Top ten major scientific progresses in China in 2015
- The nano-resolution imaging platform was awarded the first rate prize of Beijing Science and Technology in 2014
- Beamline 1W1 of BSRF started to runoperate in the couplingparasitic mode of BEPCII
- Synthesis of High Performance Polymer Materials for Field Effect-Transistors
- Surfactant molecular aggregates in green solvents
- GIXRD has played an important role in the characterization of organic thin-film transistors
Copyright © 2011 - 2012 Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility