| Quantum dots-hemin: Preparation and application in the absorption of heme iron |
| From: PublishDate:2017-06-16 Hits: |
Heme iron and non-heme iron are two forms of iron resources in diet,and approximately 70%of the total iron exists in the form of heme iron. Moreover, supplementation of heme iron is the first choice to treat iron deficiency anemia. Early in 1955, heme-derived iron was first reported to be absorbed by enterocytes. However, it is still unknown clearly the mechanism of heme iron absorption, which is mainly due to the limit of effective markers and labeling methods for heme iron. With the discovery and development of a new kind of labeling nanosmaterial - quantum dots (QDs), the group of basic and applied study of iron metabolism in Hebei Normal University labelled the heme iron with QDs. After the preparation of QDs-hemin, they were characterized and applied in the absorption of heme iron in duodenum. Their research has been published on October, 2016 in Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, biology and medicine. The team successfully prepared QDs-hemin which was found to have many advantages in the application of biology. They have a high joint efficiency of heme iron with QDs. The diameter of QDs-hemin is nanoscale and uniform. The fluorescence intensity of the QDs-hemin was stable at pH (5~9), and the fluorescence was resistant to quenching. After the injection of hemin into the duodenum loop, Micro X-ray Fluorescence (μ-XRF) and laser confocal scanning microscopy were used to observe the absorption of hemin, data found that a significant amount of iron was observed in intestinal villi 20 min after injection,and that the iron signals moved from the upper to the basolateral side of villi, even to the deeper layer of the duodenum with the increasing time after injection.
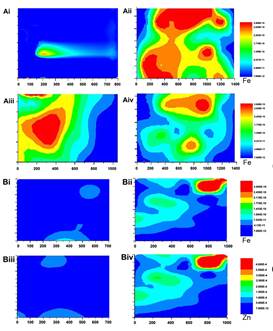
Distribution of iron and QDs-hemin detected in duodenum by μ-XRF (A) Iron distribution in duodenum after administration of hemin for different times: Ai (control), Aii (20 min), Aiii (40 min) and (Aiv) 60 min. (B) Co-distribution of iron and zinc (Biii, Biv) at 40 min after administration of QDs-hemin. Bi: iron, control; Bii: iron, QDs-hemin; Biii: zinc, control; Biv: zinc, QDs-hemin. However, it remained unclear whether the absorption of QDs-hemin was separated or as a conjugate during the absorption. Synchrotron sources at 4W1B endstation Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility can help to solve the problem, and μ-XRF technology took the absolute advantage. Because QDs contains zinc, and μ-XRF could provide the information of distribution of zinc and iron in the same section, μ-XRF images showed that both QDs-hemin group (Bii, Biv) and control group (Bi, Biii) exhibited co-distribution of iron and zinc. These data demonstrated that QDs-hemin were very stable and absorbed as an intact conjugate into the intestine. Therefore, QDs can be used as a quantitative marker to label the absorption of heme iron in real time. Their discovery will provide new strategy to investigate the mechanism of heme iron absorption in intestine. As for the mechanisms and regulatory pathway of heme iron absorption, there are still ambiguous opinions which are receptor-mediated endocytosis and hemoglobin carrier protein-1 (HCP1) mediated pathway. But there is no report which is the primary pathway for heme iron absorption. Experiments in vivo and in vitro suggested that HCP1 pathway was especially predominant in the absorption of heme iron and that QDs-hemin was degraded in lysosomes after they were absorbed by the enterocytes in the duodenum. This research identified that QDs could be used as a marker and labelling for iron absorption and transport, and also demonstrated that HCP1 pathway is the predominant to the endocytosis pathway in the absorption of heme iron. These data not only enrich the theory of intestine iron absorption, but make a further progress in the mechanism. However, many details regarding how HCP1 functions and its regulatory mechanisms in heme absorption remains to be further clarified. Article: Lina Geng, Xianglin Duan, Yan Wang, Yashuo Zhao, Guofen Gao, Delong Liu, Yan-Zhong Chang*, Peng Yu **. Quantum dots-hemin: Preparation and application in the absorption of heme iron. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, biology and medicine, 2016, 12, 1747-1755. |
|
|
| Chinese
- Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting——Top ten major scientific progresses in China in 2015
- The nano-resolution imaging platform was awarded the first rate prize of Beijing Science and Technology in 2014
- Beamline 1W1 of BSRF started to runoperate in the couplingparasitic mode of BEPCII
- Synthesis of High Performance Polymer Materials for Field Effect-Transistors
- Surfactant molecular aggregates in green solvents
- GIXRD has played an important role in the characterization of organic thin-film transistors
Copyright © 2011 - 2012 Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility