| Photo-driven hydrocarbon synthesis using cobalt metal nanoparticle catalysts derived from CoAl-LDH nanosheets |
| From: PublishDate:2020-07-30 Hits: |
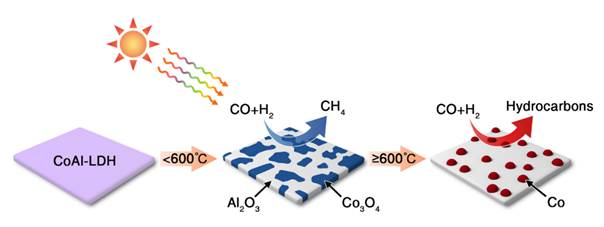
Oil is an indispensable energy for the production and life of human society. As strategic resource, it is related to a country’s economies. As a country with large energy consumption, China is rich in coal and poor in oil, which is a significant feature of energy distribution in China. How to produce a series of value-added products through raw coal is more important. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis (FTS) is based on the conversion of coal and natural gas into raw gas (CO and H2) and then further into high value-added fuel or chemicals under high temperature and high pressure. Co-based catalysts are widely used in traditional FTS as a highly efficient catalyst for the produce of higher hydrocarbons. However, in the traditional FTS, the reaction conditions are harsh, energy consumption is serious, and the environment is seriously polluted; compared with traditional thermal catalysis, the use of solar energy as an energy carrier to drive the reaction has unique advantages such as room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and is attracting attention as an ideal clean energy technology. LDH is a type of two-dimensional layered anionic compound. It is widely used in photocatalysis and electrocatalysis applications due to its advantages of adjustable interlayer ions, adjustable layer metal and adjustable layer thickness. Based on this, the team of Tierui Zhang, Institute of Physical and Chemical Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, used CoAl-LDH as the precursor for the first time to produce different types of supported Co-based catalysts under different reduction temperature by H2. This research made a detailed analysis of the performance difference of two different types of catalysts in the photo-driven CO hydrogenation, and through detailed theoretical calculations were given difference. By the detailed theoretical calculations, the difference between the two catalysts hydrogenation and carbon-carbon coupling was given. This work pave the way for the development of other photothermal catalysts for solar-driven FTS reactions. Their research has been published on March 24th, 2019 in Nano Energy.
Scheme 1. The different Co-x catalysts formed by H2 reduction of a CoAl-LDH nanosheet precursor at different temperatures. The CO hydrogenation selectivity of each Co-x catalyst is indicated. In this study, the group used CoAl-LDH as the precursor for the first time to produce different types of supported Co-based catalysts under different reduction temperature by H2(Co3O4/Al2O3 under low temperature and Co/Al2O3 under high temperature) And the performance of CO hydrogenation was investigated; the difference between the hydrogenation of two catalysts and carbon-carbon coupling was given by XAFS experiments carried out at BSRF and detailed theoretical calculations. This work provides new ideas for the use of solar to drive FTS reaction. Article: Zhenhua Li, Jinjia Liu, Yufei Zhao, Run Shi, Geoffrey I.N. Waterhouse, Yuanshen Wang, Li-Zhu Wu, Chen-Ho Tung and Tierui Zhang* Photothermal hydrocarbon synthesis using alumina-supported cobalt metal nanoparticle catalysts derived from layered-double-hydroxide nanosheets Nano Energy, 2019, 60, 467-475. |
|
|
| Chinese
- Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting——Top ten major scientific progresses in China in 2015
- The nano-resolution imaging platform was awarded the first rate prize of Beijing Science and Technology in 2014
- Beamline 1W1 of BSRF started to runoperate in the couplingparasitic mode of BEPCII
- Synthesis of High Performance Polymer Materials for Field Effect-Transistors
- Surfactant molecular aggregates in green solvents
- GIXRD has played an important role in the characterization of organic thin-film transistors
Science Highlights
Home /
Copyright © 2011 - 2012 Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility