| Ultrastable Au nanoparticles on titania achieved by an encapsulated strategy under oxidative atmosphere |
| From: PublishDate:2020-07-30 Hits: |
Supported gold catalysts play an important role in many catalytic reactions, such as CO oxidation, water-gas shift (WGS) reaction and oxidative reforming of methane. However, Au nanoparticles (NPs) are tending to sinter at high temperature because of its low Tammann temperature, resulting in poor on-stream stability. Classical strong metal-support interaction (SMSI), an important concept in heterogeneous catalysis, has been studied extensively since it was termed by Tauster et al. in the late 1970s. The classical SMSI was widely found for platinum group metals supported on reducible oxides, such as TiO2 and CeO2, upon high-temperature reduction pretreatment. However, unlike platinum group metals, it has been well-recognized for a long time that Au cannot manifest SMSI due to its low work function and low surface energy. In 2017, Junhu Wang' group demonstrated the existence of classical SMSI between Au and TiO2 for the first time and the encapsulation of Au by TiOx overlayer was also observed (Sci Adv, 2017, 3, e1700231). Whereas classical SMSI state is reversible that the formed TiOx overlayer will retreat under further oxidation pretreatment at high temperature (>400 oC), leading to invalid effect on the catalytic performance of the gold. Therefore, it is urgent to propose an original strategy to construct an overlayer containing Ti species on Au, which is endurable under oxidative atmosphere.
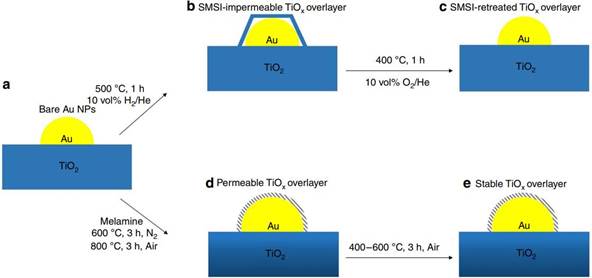
Figure 1. SMSI and melamine-induced TiOx overlayer structure and behavior. a Bare Au nanoparticles on TiO2. b Au/TiO2 catalyst that forms an impermeable SMSI TiOx overlayer after treatment with 10 vol% H2/He at 500 oC. c SMSI TiOx overlayer retreats when exposed to oxidation condition at 400 oC which is almost similar with that in a. d Melamine-modified catalyst that forms a permeable TiOx overlayer after treatment with N2 at high temperature (600 oC) followed by treatment with air at 800 oC. e Stable melamine-induced TiOx overlayer under air condition modifies the Au NPs catalytic bahavior. Here, we reported that Au NPs can be encapsulated by a permeable TiOx overlayer under oxidative atmosphere, the reverse of the condition required for classical SMSI. We found that the key to construct the above cover layer is the application of melamine and pretreatment in nitrogen condition, followed by calcination at 800 oC in air atmosphere. More importantly, this TiOx overlayer was stable upon further calcination under oxidation condition, which is contrary to the classical SMSI. X-ray adsorption spectroscopy carried out at 1W1B-XAFS station of BSRF was also employed to investigate whether new bond was formed and the fitting results revealed that new Au-Ti bond was formed when the encapsulation occurred. Owing to the formation of the overlayer, the resultant catalyst is resistant to sintering and exhibits high activity as well as excellent durability in WGS reaction and simulated practical testing. Moreover, this original strategy can be extended to colloidal Au supported on TiO2 and commercial Au supported on TiO2 gold catalyst named RR2Ti. These new findings provide a new avenue to rationally devise and develop highly stable Au catalysts with controllable activity. The research has been published on December 21th, 2019 in Nature Communications (Article number: 5790). Article: Shaofeng Liu, Wei Xu, Yiming Niu, Bingsen Zhang, Lirong Zheng, Wei Liu, Lin Li, Junhu Wang* Ultrastable Au nanoparticles on titania through an encapsulation strategy under oxidative atmosphere. Nature Communications 10 (2019) 5790. |
|
|
| Chinese
- Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting——Top ten major scientific progresses in China in 2015
- The nano-resolution imaging platform was awarded the first rate prize of Beijing Science and Technology in 2014
- Beamline 1W1 of BSRF started to runoperate in the couplingparasitic mode of BEPCII
- Synthesis of High Performance Polymer Materials for Field Effect-Transistors
- Surfactant molecular aggregates in green solvents
- GIXRD has played an important role in the characterization of organic thin-film transistors
Copyright © 2011 - 2012 Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility