| The role of cupric ions in the oxidative dissolution process of marmatite: A dependence on Cu2+ concentration |
| From: PublishDate:2020-07-31 Hits: |
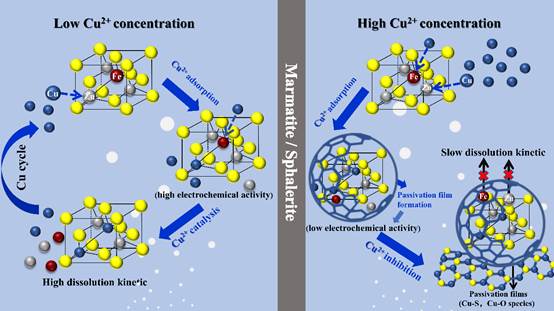
Marmatite (iron containing sphalerite) is one of the most abundant Zn-bearing resources on earth, which has an important position in the zinc industry. Marmatite frequently occur in ore deposits associated with the other metal sulfides like copper sulfides (such as chalcopyrite, bornite and chalcocite). It is a challenge to separate complex copper-zinc ores deeply in flotation, because cupric ions can significantly active marmatite flotation. Hence, cupric ions always cannot be avoided in the hydrometallurgical process of marmatite. Meanwhile, the oxidative dissolution of abandoned wastes containing marmatite will release heavy metal ions and cause environmental contamination. Hence, the reaction mechanism and intermediate products during the dissolution process of marmatite in the presence of cupric ions are important but still not certain. A team from Key Lab of Biohydrometallurgy of Ministry of Education of Central South University investigated the role of cupric ions in the dissolution process of marmatite and the reaction mechanism. The research results have been published in Science of the Total Environment, on July 20, 2019. The research team found that the role of cupric ions in marmatite dissolution was significantly dependent on cupric ions concentration. A low Cu2+ concentration (0.25-750 mg/L) can significantly accelerate marmatite dissolution, and a relatively high Cu2+ concentration (above 1000 mg/L) hindered marmatite dissolution.
Leaching residue was analyzed by the experiments data obtained at Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility (BSRF). It was found that characteristic peak belonging to the Cu-S phase was not detected in the residue, confirming that the reaction between copper ions and marmatite was surface reaction. The proportion of copper and polysulfide (Sn2-) was significantly increased within 10 nm of the residue surface, as the concentration of copper ions in the solution increased. This work provides scientific ideas and references for controlling the dissolution process of marmatite in the presence of cupric ions, and is important for both hydrometallurgy and environment protection. Synchrotron sources have helped the team reveal the specific mechanism of cupric ions in marmatite dissolution. “The role of cupric ions in marmatite dissolution significantly depends on its concentration. The adsorption products at low cupric ions concentration can improve the electrochemical reactivity of marmatite, thus promoting its dissolution process. However, a passivation layer mainly consisting of Cu-S, Cu-O and Cu-Sn species formed due to the high percentage of Cu2+ adsorption. The passivation layer decreased the electrochemical reactivity of marmatite surface, thus resulting in hindering the oxidative dissolution of marmatite. The higher energy synchrotron radiation beam line definitely assist us in determining the intermediate products”, explained by Hongbo Zhao, professor from Key Lab of Biohydrometallurgy of Ministry of Education, Central South university. Article: Xiaoyu Meng, Hongbo Zhao*, Menglin Sun, Yisheng Zhang, Yanjun Zhang, Xin Lv, Shuai Wang*, Guanzhou Qiu , Role of cupric ions in the oxidative dissolution process of marmatite: a dependence on Cu2+ concentrations. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 675:213-223. |
|
|
| Chinese
- Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting——Top ten major scientific progresses in China in 2015
- The nano-resolution imaging platform was awarded the first rate prize of Beijing Science and Technology in 2014
- Beamline 1W1 of BSRF started to runoperate in the couplingparasitic mode of BEPCII
- Synthesis of High Performance Polymer Materials for Field Effect-Transistors
- Surfactant molecular aggregates in green solvents
- GIXRD has played an important role in the characterization of organic thin-film transistors
Science Highlights
Home /
Copyright © 2011 - 2012 Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility