News and Events
Science Highlights
Home /
|
|
|
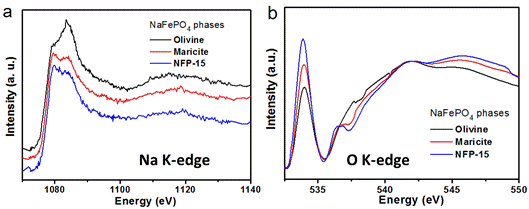
Among the various SIBs cathode materials, NaFePO4 attracts much attention owing to its high theoretical capacity (155 mAh g-1), low cost, high structural stability, and non-toxicity. Nevertheless, the NaFePO4 with maricite structure, thermodynamically stable phase, has been considered as electrochemically inactive for sodium-ion storage. A team from State Key Laboratory of Silicate Materials for Architectures of W...
|
|
|
|
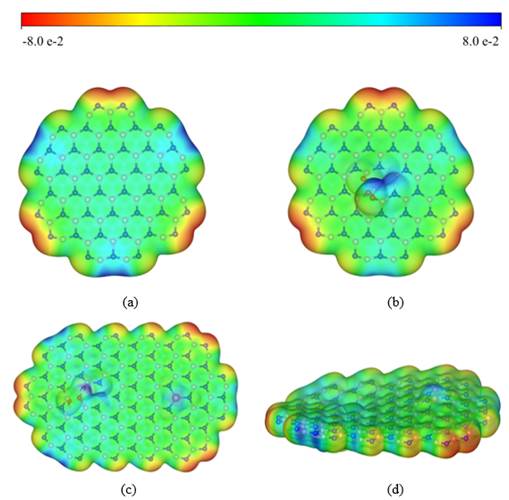
A team from Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed an innovative preparation method of Cu-doped boron nitride nanobelts (Cu-BN) and gained insight into the structure-activity relationship of the catalyst in Fenton system. Their research has been published on Journal of Materials Chemistry A in 2019.
|
|
|
|
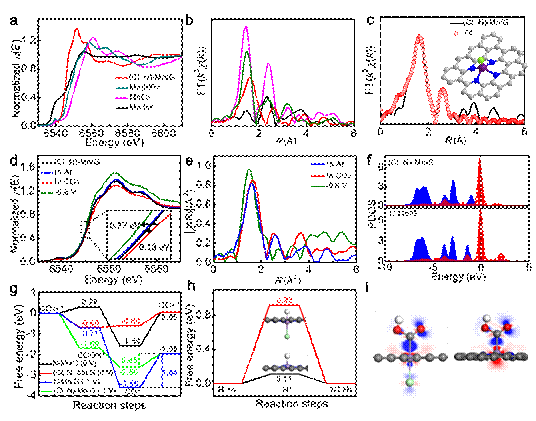
Excessive consumption of fossil fuels causes huge energy and environmental problems. The electrocatalytic CO2 conversion to high-value fuels and chemicals provides an ideal way to alleviate the energy and environmental problems. Particularly, the development of cheap and earth-abundant electrocatalysts is of great significance. A team from Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, conducted in-depth res...
|
|
|
|
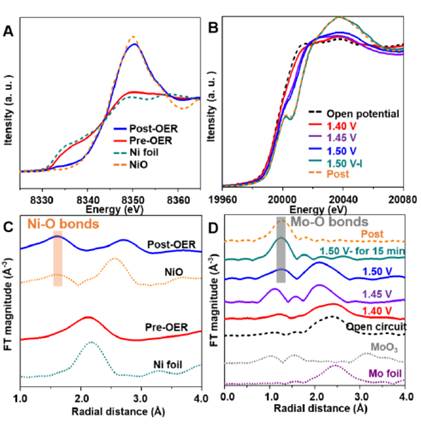
The oxygen evolution reaction (OER) of electrochemical water splitting is the key process in solar-to-chemical conversion technologies, but the kinetics of OER is sluggish, even when facilitated by high-efficiency precious-metal-containing catalysts. Therefore, it is very important to explore high-activity, robust-stability, and low-cost catalysts. In general, the activities of metal compounds based OER catalysts ...
|
|
|
|
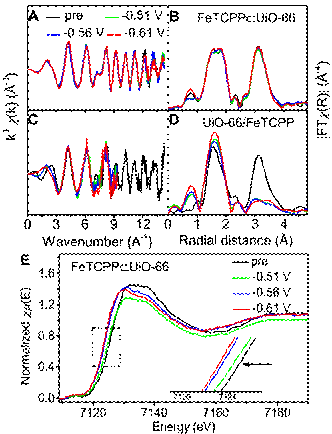
Electrochemical reduction of CO2 can transform CO2 into useful chemicals and fuels by using renewable electric energy and water, which is an ideal energy utilization strategy. However, CO2 reduction generally need a high potential to derive and the side reactions of hydrogen evolution always occur concomitantly. It has become a critical issue to develop highly selective and active electrocatalysts. The CO2 reducti...
|
|
|
|
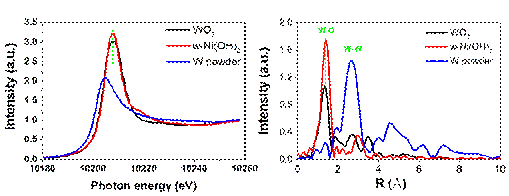
Electrocatalytic water splitting for oxygen generation is an multi-electron, multi-step process. The water adsorption and the formation of oxygen-producing intermediates are the main reason for the relative big overpotential. How to control the surface sites for promoting the water oxidation steps is one difficulty. A team from New Energy Research Institute of Shanxi Normal University use the W6+ for doing into α...
|

Copyright © 2011 - 2012 Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility